In today’s fast-paced world, the significance of diet and nutrition often takes a backseat. However, the food we consume plays a pivotal role in determining not just our physical health, but our mental and emotional well-being as well. As the old adage goes, “You are what you eat.” This statement holds profound truth, emphasizing the direct correlation between our dietary choices and overall health.
The importance of diet and nutrition transcends beyond mere sustenance. It’s about fueling our bodies with the right kind of nutrients, ensuring optimal functionality and longevity.
Every bite we take is a step towards either enhancing our health or detracting from it. With the rise in chronic diseases, obesity, and mental health issues, there has never been a more crucial time to understand and appreciate the profound impact of our dietary choices.
Moreover, nutrition is not just about preventing illness; it’s about thriving. A well-balanced diet can boost energy levels, enhance cognitive function and even elevate mood. The foods we choose to consume can be our most potent medicine or our slowest poison.
As we delve deeper into this guide, we will explore the foundational principles of diet and nutrition, understand their role in our overall health, and provide actionable insights to make informed and healthful choices. Whether you’re a seasoned nutrition enthusiast or just beginning your health journey, this article aims to offer valuable knowledge and inspire a renewed commitment to optimal health and wellness through mindful eating.
The Basics of Diet and Nutrition
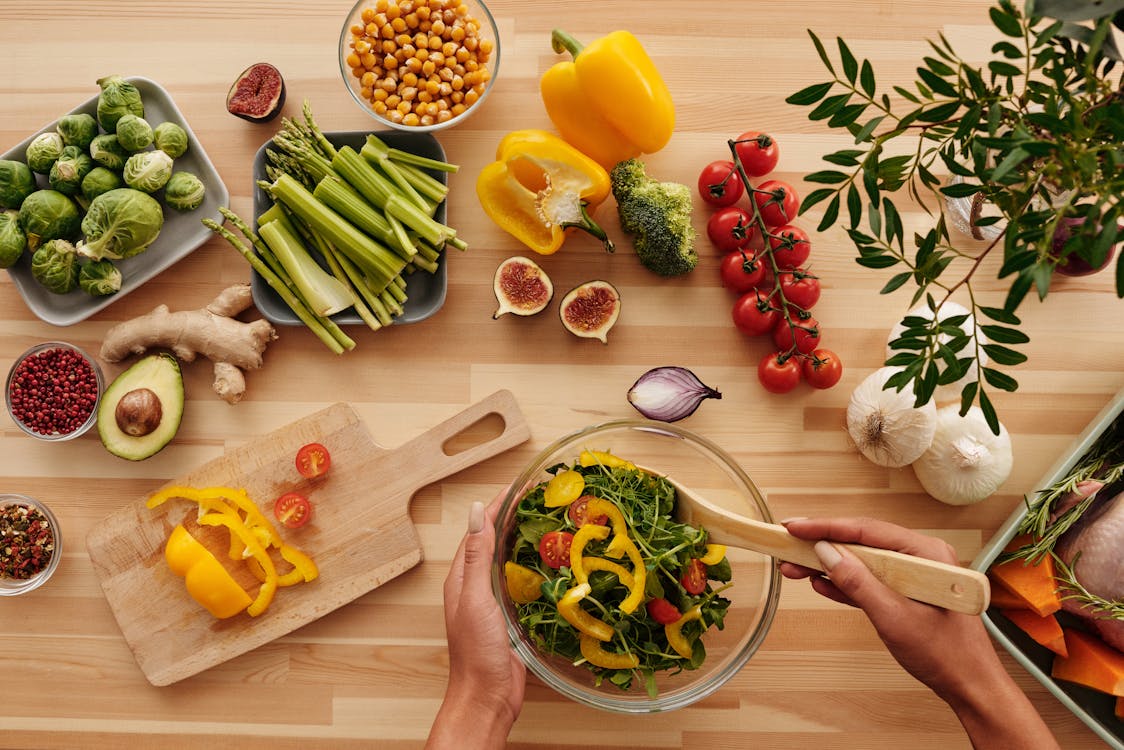

Understanding the fundamentals of diet and nutrition is the first step towards making informed choices that can transform our health. At its core, nutrition is the science of how our bodies utilize the food we eat, converting it into energy and building blocks for growth and repair.
Definition of Diet and Nutrition:
- Diet: Refers to the combination of foods and drinks consumed by an individual on a daily basis. It encompasses everything we eat and drink, from meals to snacks and beverages.
- Nutrition: The process by which our body takes in and utilizes the nutrients from the foods we consume. It involves digestion, absorption, transportation and utilization of these nutrients.
The Role of Macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates: The primary source of energy for our bodies. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels our cells, tissues and organs. Sources include grains, fruits, vegetables and legumes.
- Proteins: Essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. Proteins are made up of amino acids, the building blocks of our body. Sources include meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, and plant-based alternatives like tofu and legumes.
- Fats: A concentrated source of energy and essential for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K). Healthy sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil and fatty fish.
The Significance of Micronutrients:
- Vitamins: Organic compounds required in small amounts for various physiological functions. Each vitamin has a specific role, from boosting immunity (Vitamin C) to aiding in blood clotting (Vitamin K).
- Minerals: Inorganic nutrients that play a crucial role in various bodily functions, such as bone health (calcium) and oxygen transport (iron).
A balanced diet is one that provides all the essential macronutrients and micronutrients in appropriate proportions. It’s not just about eating the right quantity of food, but also ensuring the quality and diversity of nutrients.
The Impact of Diet on Physical Health
The foods we consume have a direct and profound impact on our physical health. From the strength of our bones to the rhythm of our heartbeats, every aspect of our bodily function is influenced by our dietary choices.
Weight Management and the Role of a Balanced Diet:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a variety of foods from all food groups in the right proportions ensures that we get all the essential nutrients without excess calories.
- Caloric Balance: The equilibrium between calories consumed through diet and calories expended through physical activity. Maintaining this balance is crucial for weight stability.
- Impact of Overeating: Consuming more calories than the body needs can lead to weight gain, increasing the risk of obesity and associated health issues.
- Benefits of a Healthy Weight: Reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved mobility, better sleep quality and increased lifespan.
Prevention of Chronic Diseases:
- Heart Disease: A diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk of heart disease by managing cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- Diabetes: Consuming a balanced diet with controlled sugar and refined carbohydrate intake can prevent type 2 diabetes and manage blood sugar levels for those already diagnosed.
- Hypertension: Reducing salt intake and focusing on potassium-rich foods like bananas and spinach can help regulate blood pressure.
Boosting Immunity and Resistance to Illnesses:
- Vital Nutrients: Vitamins C, E, A, and minerals like zinc and selenium play a crucial role in strengthening the immune system.
- Gut Health: A diet rich in fiber and fermented foods promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which is closely linked to immune function.
- Antioxidants: Foods like berries, nuts, and green tea are packed with antioxidants that combat free radicals and protect the body from infections.
Our diet acts as the frontline defense against various health challenges. By making informed and healthful dietary choices, we can fortify our bodies, enhance resilience against diseases, and pave the way for a life of vitality and wellness.
Nutrition and Mental Well-being
While the physical benefits of a balanced diet are widely recognized, the profound influence of nutrition on our mental health is often overlooked. The foods we consume can directly impact our mood, cognition and overall mental well-being.
The Brain-Gut Connection:
- The Second Brain: The gut is often referred to as the “second brain” due to its intricate network of neurons and the production of neurotransmitters.
- Gut Microbiome: A healthy gut flora, influenced by our diet, plays a pivotal role in producing serotonin, a neurotransmitter responsible for mood regulation.
- Dietary Impact: Consuming probiotics, prebiotics, and fiber-rich foods can promote a healthy gut microbiome, subsequently enhancing mental well-being.
Nutrients Essential for Brain Health:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, these fats are crucial for brain function and have been linked to reduced depression and cognitive decline.
- B Vitamins: Especially B6, B9 (folate), and B12, play a role in producing brain chemicals that affect mood. Deficiencies can lead to depression. Sources include leafy greens, legumes, and fortified cereals.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries, dark chocolate, and nuts, protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can be detrimental to brain health.
The Role of Hydration in Cognitive Function:
- Brain Function: Even mild dehydration can impair attention, short-term memory and mood.
- Daily Intake: While the exact amount varies based on individual needs, aiming for at least 8 glasses of water daily is a general guideline.
- Other Sources: Fruits and vegetables, herbal teas, and broths also contribute to daily hydration.
The adage “food for thought” holds literal significance. Our dietary choices not only nourish our bodies but also our minds. By understanding the intricate relationship between nutrition and mental health, we can make empowered choices that uplift our spirits, sharpen our minds, and foster emotional resilience.
Specialized Diets and Their Benefits
In the realm of nutrition, various specialized diets have gained popularity over the years. These diets, often rooted in cultural, ethical, or health-based principles, offer unique benefits and cater to specific needs and preferences.
Veganism and Vegetarianism:
- Overview: Vegan diets exclude all animal products, while vegetarian diets exclude meat but may include dairy and eggs.
- Health Benefits: Lower risk of heart disease, hypertension, type 2 diabetes and certain cancers. Additionally, these diets often lead to lower cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
- Environmental Perspective: Adopting a plant-based diet can reduce the environmental footprint, as animal agriculture is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation and water consumption.
- Ethical Considerations: Many choose these diets based on concerns for animal welfare and ethical treatment.
The Mediterranean Diet:
- Overview: Inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, this diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, fish, and moderate wine consumption.
- Benefits: Associated with reduced risks of heart disease, stroke, and Alzheimer’s disease. It also promotes longevity and overall well-being.
- Key Components: High in healthy fats, low in red meat and rich in antioxidants.
Ketogenic Diet:
- Overview: A high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet that shifts the body’s metabolism from burning glucose to burning fats (ketones) for energy.
- Potential Benefits: Weight loss, improved blood sugar and insulin levels, and potential neuroprotective effects. Some studies suggest it may benefit certain neurological disorders.
- Considerations: While many find success with the keto diet, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting, as it may not be suitable for everyone.
While specialized diets offer various benefits, it’s crucial to remember that individual needs and responses can vary. What works for one person might not work for another. It’s always recommended to consult with a nutritionist or healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes to ensure they align with individual health goals and requirements.
The Role of Supplementation
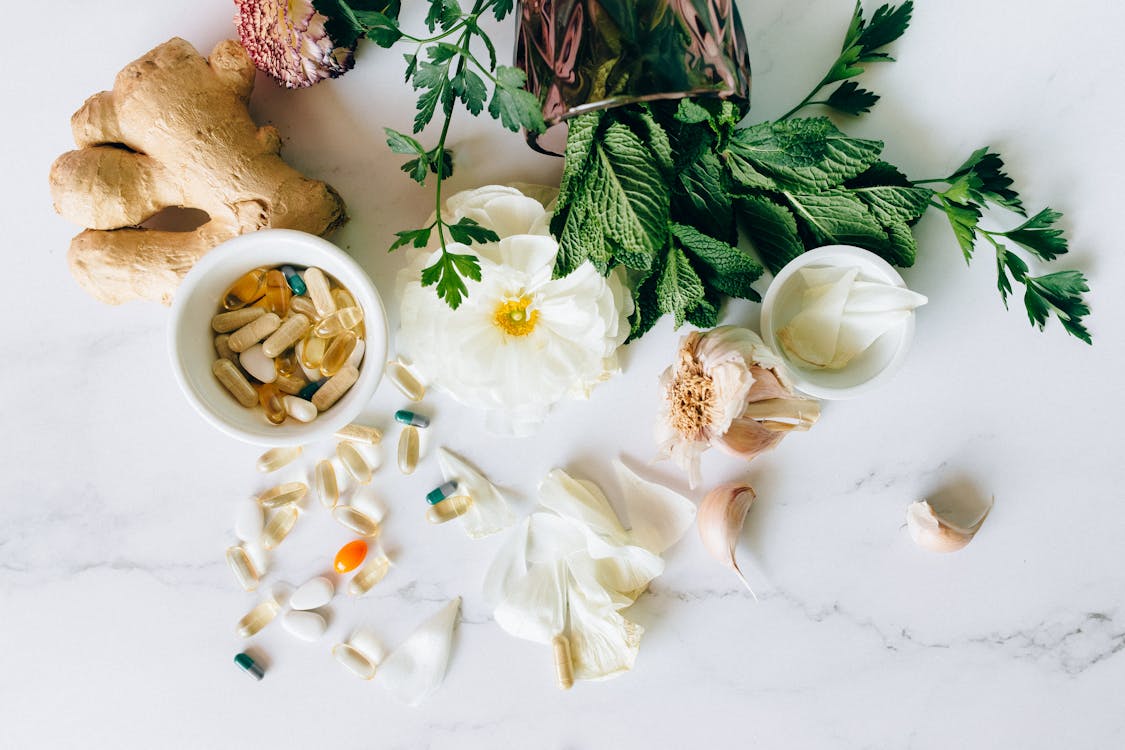

While a balanced diet should ideally provide all the essential nutrients our bodies need, there are instances where supplementation can be beneficial. Dietary supplements can fill nutritional gaps, cater to specific health needs and enhance overall well-being.
When and Why to Consider Dietary Supplements:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Despite best efforts, some individuals may struggle to get certain nutrients from food alone, such as vitamin D during winter months or vitamin B12 for vegans.
- Life Stages: Pregnant women may require folic acid, iron, and calcium supplements. Older adults might benefit from vitamin D and B12 supplements.
- Medical Conditions: Certain health issues or medications can interfere with nutrient absorption, necessitating supplementation.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Popular Supplements:
- Multivitamins: Can provide a broad spectrum of nutrients, beneficial for those with varied deficiencies. However, excessive intake can lead to nutrient imbalances.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Beneficial for heart health, brain function and inflammation reduction. Sources include fish oil and algal oil.
- Probiotics: Support gut health and digestion. Different strains offer varied benefits, so it’s essential to choose the right one for individual needs.
- Vitamin D: Supports bone health, immune function, and mood regulation. Especially important for those with limited sun exposure.
- Caution: Over-reliance on supplements can lead to excessive intake, which might be harmful. It’s crucial to remember that supplements should complement a diet, not replace it.
The Importance of Consulting with Healthcare Professionals:
- Personalized Recommendations: A healthcare provider can offer guidance on the right type and dosage of supplements based on individual health profiles.
- Safety Concerns: Some supplements can interact with medications or have side effects. Professional guidance ensures safe and effective use.
- Quality Assurance: Not all supplements are created equal. A healthcare professional can recommend reputable brands that adhere to quality standards.
While dietary supplements can offer numerous benefits, they should be approached with caution and knowledge. They are not a substitute for a balanced diet but can be a valuable tool in achieving optimal health when used appropriately.
The Connection Between Diet, Exercise, and Sleep
Diet, exercise, and sleep form the triad of holistic health. Each component influences the other, creating a synergistic relationship that determines our overall well-being. Understanding the interplay between these elements can help us optimize our health and lead a balanced life.
The Synergistic Relationship:
- Energy and Endurance: A nutritious diet fuels our workouts, providing the energy and stamina required for physical activities.
- Recovery and Repair: Post-exercise, our bodies rely on nutrients, especially proteins and certain minerals, to repair tissues and build muscles.
- Sleep and Restoration: Quality sleep allows the body to recover from physical exertion and prepares it for the next day. A balanced diet can influence sleep quality and duration.
How Diet Can Optimize Athletic Performance:
- Carbohydrates: The primary energy source for high-intensity workouts. Consuming carbs before exercise can boost performance.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle growth and repair. Post-workout protein intake can aid in recovery and muscle building.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for endurance and peak performance. Even mild dehydration can impair athletic abilities.
- Micronutrients: Minerals like potassium and magnesium help prevent muscle cramps and fatigue.
The Role of Nutrition in Recovery and Muscle Growth:
- Recovery Foods: Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries and nuts, can reduce muscle soreness and inflammation post-exercise.
- Muscle Growth: Amino acids from protein sources are the building blocks of muscles. Consuming protein-rich foods post-exercise supports muscle synthesis.
- Sleep and Growth: Growth hormone, essential for muscle development, is released during deep sleep. Thus, quality sleep is crucial for those looking to build muscle mass.
Diet’s Influence on Sleep Patterns:
- Tryptophan-Rich Foods: Foods like turkey, milk, and bananas contain tryptophan, an amino acid that promotes sleep.
- Caffeine and Sleep: Consuming caffeine late in the day can disrupt sleep patterns. It’s advisable to limit caffeine intake in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Balanced Meals: Heavy, spicy, or acidic meals can cause discomfort and indigestion, disrupting sleep. Opt for light, balanced dinners for better sleep quality.
The intricate relationship between diet, exercise, and sleep underscores the importance of a holistic approach to health. By recognizing and respecting this triad, we can achieve a state of balance, vitality and optimal well-being.
Embracing Mindful Eating for Holistic Wellness
In our fast-paced world, meals often become rushed affairs, consumed while multitasking or on the go. However, embracing the practice of mindful eating can transform our relationship with food, leading to better health, improved digestion, and a deeper appreciation for the nourishment we receive.
What is Mindful Eating?
- Definition: Mindful eating is the practice of being fully present during meals, savoring each bite, and listening to the body’s hunger and fullness cues.
- Beyond Just Eating: It’s a holistic approach that encompasses the entire eating experience, from choosing and preparing food to consuming and reflecting on the meal.
Benefits of Mindful Eating:
- Improved Digestion: Eating slowly and chewing thoroughly aids in digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Weight Management: By tuning into hunger and fullness cues, one can avoid overeating and make healthier food choices.
- Enhanced Enjoyment: Savoring each bite allows for a deeper appreciation of flavors, textures and the overall joy of eating.
- Reduced Stress: Taking the time to eat mindfully can be a form of meditation, reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
Tips for Practicing Mindful Eating:
- Distraction-Free Meals: Avoid eating in front of the TV or while using electronic devices. Create a calm environment for meals.
- Savor Each Bite: Focus on the flavors, textures, and aromas of the food. Appreciate the nourishment it provides.
- Listen to Your Body: Recognize the difference between physical hunger and emotional cravings. Eat when genuinely hungry and stop when satisfied.
- Gratitude Practice: Before eating, take a moment to express gratitude for the meal and the hands that prepared it. This can enhance the eating experience and foster a deeper connection to food.
The Bigger Picture:
- Holistic Health: Mindful eating is more than just a dietary practice; it’s a philosophy that promotes holistic health, mindfulness, and living in the present moment.
- Connection to Food: Understanding the source of our food, the effort that goes into its production, and its impact on our health fosters a deeper connection and respect for what we consume.
Mindful eating is a journey of self-discovery, awareness, and appreciation. By embracing this practice, we can transform our relationship with food, nurture our bodies, and cultivate a sense of gratitude and presence in our daily lives.
The Future of Nutrition: Trends and Innovations

As science and technology advance, the field of nutrition is undergoing rapid transformations. From personalized nutrition plans based on genetics to sustainable food production, the future of nutrition promises exciting innovations that will reshape the way we view and interact with our food.
Personalized Nutrition:
- Genetic-Based Diets: With advancements in genomics, it’s becoming possible to tailor diets based on individual genetic profiles, optimizing health outcomes.
- Microbiome Analysis: Understanding one’s gut microbiome can lead to personalized probiotic and dietary recommendations to enhance gut health and overall well-being.
- Wearable Tech: Devices that monitor blood sugar levels, hydration status, and other vital metrics in real-time can provide instant dietary feedback and recommendations.
Sustainable and Ethical Food Production:
- Lab-Grown Meat: A potential solution to the environmental and ethical concerns of traditional meat production, lab-grown or cultured meat is produced from animal cells without the need to raise and slaughter animals.
- Vertical Farming: Growing crops in stacked layers, often in urban environments, can reduce the carbon footprint of food production and ensure a fresher, more local food supply.
- Plant-Based Alternatives: The rise of plant-based meats, dairy, and other alternatives cater to the growing demand for sustainable and cruelty-free food options.
Nutritional Technologies and Innovations:
- 3D Food Printing: Creating customized, nutrient-dense foods using 3D printing technology can cater to specific dietary needs and preferences.
- Nano-Nutrition: Using nanotechnology to enhance the bioavailability and absorption of nutrients, ensuring maximum health benefits.
- Smart Packaging: Packaging that changes color when food is spoiled or that releases preservatives to extend shelf life can reduce food waste and ensure food safety.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence:
- Dietary Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots that provide real-time dietary advice, meal planning and nutritional information.
- Predictive Health Analysis: Using AI to analyze dietary habits, health metrics, and genetic data to predict potential health issues and provide preventive dietary recommendations.
The future of nutrition is poised at the intersection of science, technology, and human well-being. As we move forward, these innovations ppexels.com/…/two-women-making-a-healthy-drink-6707696romise not only to enhance our health but also to revolutionize our relationship with food, making it more sustainable, personalized and in tune with our individual needs.
Conclusion: The Holistic Approach to Nutrition and Well-being

Diet and nutrition are more than just the foods we consume; they are the foundation of our overall health, vitality, and well-being. As we’ve explored throughout this article, the choices we make in our daily diets have profound impacts on our physical health, mental well-being, and even our environmental footprint.
From understanding the basics of macronutrients and micronutrients to embracing mindful eating and navigating the vast sea of nutritional information, it’s evident that a holistic approach is essential.
The future of nutrition is exciting, with innovations and trends promising personalized and sustainable solutions. However, with the abundance of information available, it’s crucial to stay informed, discerning, and open-minded. By doing so, we can make empowered decisions that not only nourish our bodies but also nurture our minds and souls.
In the end, the journey to optimal health and wellness is deeply personal. It’s about finding balance, listening to our bodies, and making choices that resonate with our individual needs, values and aspirations. As we continue on this path, let us remember that every meal is an opportunity—a chance to nourish, heal, and celebrate the beautiful act of living.
Discover a healthier vaping experience with the best nicotine-free vapes of 2023 at No Nic Vapes – your guide to a nicotine-free future!
Further Reading:
“Diet & Nutrition” – A comprehensive set of articles that cover various aspects of diet and nutrition. They provide insights into healthy eating habits, the role of nutrients and the importance of hydration. Read the articles here
“Diet and Nutrition Tips for Women” – Specifically tailored for women, this article delves into the unique nutritional needs of women at different life stages. It provides guidance on essential nutrients, healthy eating habits, and managing weight. Read the article here
“Diet & Nutrition” – Another informative piece that sheds light on the relationship between diet, nutrition and health. It offers advice on making healthier food choices and understanding the nutritional value of different foods. Read the article here

